PRO-Cap
Precision Nuclear Run-on Sequencing for RNA Polymerase II Start Sites
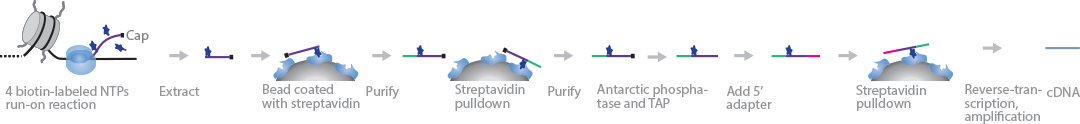
PRO-cap maps RNAPII initiation sites during RNA transcription with base-pair resolution. This approach is a variation of the PRO-Seq method, which maps RNAPII pause sites (Kwak et al., 2013). A nuclear run-on reaction with biotin-NTP and sarkosyl is carried out on nuclear lysates. Incorporation of the first biotin-NTP halts further elongation of nascent RNA strands by RNAPII. The RNA strands are extracted and purified through streptavidin pull-down. Next, 3′ adapters are ligated directly to the purified sample before another streptavidin purification step. The 5′ ends are repaired using Antarctic phosphatase and TAP before ligating 5′ adapters. The adapter-flanked RNA fragments are enriched through another streptavidin pull-down process before RT and PCR amplification. The resultant cDNA strands are sequenced from the 5′ end, and RNAPII pause sites are mapped.
Advantages:
- Maps RNAPII initiation sites with base-pair resolution
- Multiple biotin enrichment steps before PCR
- Pause sites mapped using PRO-seq
Disadvantages:
- Limited to in vitro reactions
Reagents:
Illumina Library prep and Array Kit Selector
Reviews:
Brent M. R. Past Roadblocks and New Opportunities in Transcription Factor Network Mapping. Trends Genet. 2016;32:736-750
Engreitz J. M., Haines J. E., Perez E. M., Munson G., Chen J., et al. Local regulation of gene expression by lncRNA promoters, transcription and splicing. Nature. 2016;539:452-455
References:
Wang I. X., Core L. J., Kwak H., Brady L., Bruzel A., et al. RNA-DNA differences are generated in human cells within seconds after RNA exits polymerase II. Cell Rep. 2014;6:906-915
Danko C. G., Hyland S. L., Core L. J., Martins A. L., Waters C. T., et al. Identification of active transcriptional regulatory elements from GRO-seq data. Nat Methods. 2015;
Core L. J., Martins A. L., Danko C. G., Waters C. T., Siepel A., et al. Analysis of nascent RNA identifies a unified architecture of initiation regions at mammalian promoters and enhancers. Nat Genet. 2014;
Related
History: PRO-Cap
Revision by sbrumpton on 2017-06-21 07:50:24 - Show/Hide
Precision Nuclear Run-on Sequencing for RNA Polymerase II Start Sites

PRO-cap maps RNAPII initiation sites during RNA transcription with base-pair resolution. This approach is a variation of the PRO-Seq method, which maps RNAPII pause sites (Kwak et al., 2013). A nuclear run-on reaction with biotin-NTP and sarkosyl is carried out on nuclear lysates. Incorporation of the first biotin-NTP halts further elongation of nascent RNA strands by RNAPII. The RNA strands are extracted and purified through streptavidin pull-down. Next, 3' adapters are ligated directly to the purified sample before another streptavidin purification step. The 5' ends are repaired using Antarctic phosphatase and TAP before ligating 5' adapters. The adapter-flanked RNA fragments are enriched through another streptavidin pull-down process before RT and PCR amplification. The resultant cDNA strands are sequenced from the 5' end, and RNAPII pause sites are mapped.
Advantages:- Maps RNAPII initiation sites with base-pair resolution
- Multiple biotin enrichment steps before PCR
- Pause sites mapped using PRO-seq
Disadvantages:- Limited to in vitro reactions
Reagents:Illumina Library prep and Array Kit SelectorReviews:Brent M. R. Past Roadblocks and New Opportunities in Transcription Factor Network Mapping. Trends Genet. 2016;32:736-750Engreitz J. M., Haines J. E., Perez E. M., Munson G., Chen J., et al. Local regulation of gene expression by lncRNA promoters, transcription and splicing. Nature. 2016;539:452-455References:Wang I. X., Core L. J., Kwak H., Brady L., Bruzel A., et al. RNA-DNA differences are generated in human cells within seconds after RNA exits polymerase II. Cell Rep. 2014;6:906-915Danko C. G., Hyland S. L., Core L. J., Martins A. L., Waters C. T., et al. Identification of active transcriptional regulatory elements from GRO-seq data. Nat Methods. 2015;Core L. J., Martins A. L., Danko C. G., Waters C. T., Siepel A., et al. Analysis of nascent RNA identifies a unified architecture of initiation regions at mammalian promoters and enhancers. Nat Genet. 2014;
