SPARE
Specific Parallel Amplification of 5′ RNA Ends
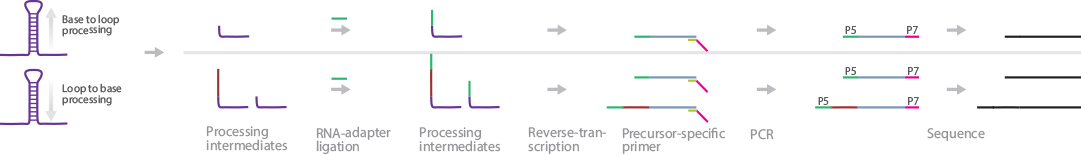
SPARE identifies genome-wide miRNA processing intermediates in plants (Schapire et al., 2013). SPARE infers the directionality of miRNA processing (base-to-loop or loop-to-base) by analyzing the resultant cDNA sequences. If only the first cleavage position is detected, the miRNA was processed in a base-to-loop fashion; however, if all cleavage intermediates are detected, it was processed in a loop-to-base fashion.
Briefly, total RNA is depleted of rRNA, and RNA adapters are ligated to the 5′ ends of uncapped RNAs. These ligated RNAs are used as the template in reverse transcription using miRNA precursor_specific primers with generic adapter tails as RT primers. The resultant cDNAs are PCR-amplified, size-selected, and sequenced.
Similar methods: PARE, 5′ RACE
Advantages:
- Enables genome-wide identification of miRNA intermediates
- Able to infer processing directionality through sequence analysis
- Less time-consuming than existing methods
- Optimized for plant genomes
Disadvantages:
- Not yet adopted widely by the scientific community
Reagents:
Illumina Library prep and Array Kit Selector
Reviews:
Ma X., Tang Z., Qin J. and Meng Y. The use of high-throughput sequencing methods for plant microRNA research. RNA Biol. 2015;12:709-719
References:
Schmidt S. A., Foley P. L., Jeong D. H., et al. Identification of SMG6 cleavage sites and a preferred RNA cleavage motif by global analysis of endogenous NMD targets in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:309-323
Related
History: SPARE
Revision by sbrumpton on 2017-06-21 07:50:23 - Show/Hide
Specific Parallel Amplification of 5' RNA Ends

SPARE identifies genome-wide miRNA processing intermediates in plants (Schapire et al., 2013). SPARE infers the directionality of miRNA processing (base-to-loop or loop-to-base) by analyzing the resultant cDNA sequences. If only the first cleavage position is detected, the miRNA was processed in a base-to-loop fashion; however, if all cleavage intermediates are detected, it was processed in a loop-to-base fashion.
Briefly, total RNA is depleted of rRNA, and RNA adapters are ligated to the 5' ends of uncapped RNAs. These ligated RNAs are used as the template in reverse transcription using miRNA precursor_specific primers with generic adapter tails as RT primers. The resultant cDNAs are PCR-amplified, size-selected, and sequenced.
Similar methods: PARE, 5' RACE
Advantages:- Enables genome-wide identification of miRNA intermediates
- Able to infer processing directionality through sequence analysis
- Less time-consuming than existing methods
- Optimized for plant genomes
Disadvantages:- Not yet adopted widely by the scientific community
Reagents:Illumina Library prep and Array Kit SelectorReviews:Ma X., Tang Z., Qin J. and Meng Y. The use of high-throughput sequencing methods for plant microRNA research. RNA Biol. 2015;12:709-719References:Schmidt S. A., Foley P. L., Jeong D. H., et al. Identification of SMG6 cleavage sites and a preferred RNA cleavage motif by global analysis of endogenous NMD targets in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:309-323
