PARS-Seq
Parallel Analysis of RNA Structure
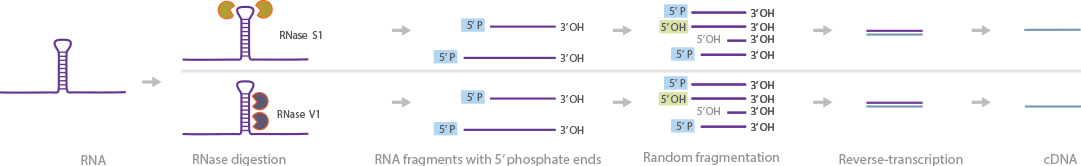
PARS-Seq mapping provides information about the secondary and tertiary structure of RNA (Wan et al., 2013). In this method, RNA is digested with RNases that are specific for double-stranded and single-stranded RNA, respectively. The resulting fragments are reverse-transcribed to cDNA. Deep sequencing of the cDNA provides high-resolution sequences of the RNA. The RNA structure can be deduced by comparing the digestion patterns of the various RNases.
Advantages:
- Provides RNA structural information
- Distinguishes between paired and unpaired bases
- Alternative to mass spectrometry, NMR, and crystallography
Disadvantages:
- Enzyme digestion can be nonspecific
- Digestion conditions must be carefully controlled
- RNA can be overdigested
- Limited to in vitro applications
Reagents:
Illumina Library prep and Array Kit Selector
Reviews:
Nussbacher J. K., Batra R., Lagier-Tourenne C. and Yeo G. W. RNA-binding proteins in neurodegeneration: Seq and you shall receive. Trends Neurosci. 2015;38:226-236
References:
Righetti F., Nuss A. M., Twittenhoff C., et al. Temperature-responsive in vitro RNA structurome of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:7237-7242
Related
History: PARS-Seq
Revision by sbrumpton on 2017-06-21 07:50:23 - Show/Hide
Parallel Analysis of RNA Structure

PARS-Seq mapping provides information about the secondary and tertiary structure of RNA (Wan et al., 2013). In this method, RNA is digested with RNases that are specific for double-stranded and single-stranded RNA, respectively. The resulting fragments are reverse-transcribed to cDNA. Deep sequencing of the cDNA provides high-resolution sequences of the RNA. The RNA structure can be deduced by comparing the digestion patterns of the various RNases.
Advantages:- Provides RNA structural information
- Distinguishes between paired and unpaired bases
- Alternative to mass spectrometry, NMR, and crystallography
Disadvantages:- Enzyme digestion can be nonspecific
- Digestion conditions must be carefully controlled
- RNA can be overdigested
- Limited to in vitro applications
Reagents:Illumina Library prep and Array Kit SelectorReviews:Nussbacher J. K., Batra R., Lagier-Tourenne C. and Yeo G. W. RNA-binding proteins in neurodegeneration: Seq and you shall receive. Trends Neurosci. 2015;38:226-236References:Righetti F., Nuss A. M., Twittenhoff C., et al. Temperature-responsive in vitro RNA structurome of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:7237-7242
