BruDRB-Seq
Bromouridine 5,6-dichlorobenzimidazole1-b-D-ribofuranoside Sequencing
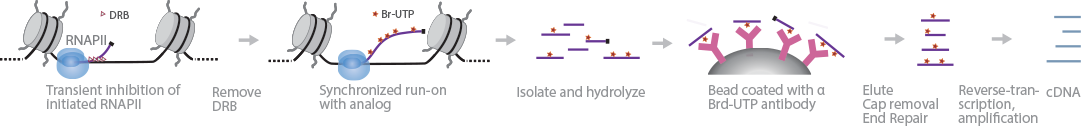
BruDRB-Seq reports the elongation rate of RNAPII (Veloso et al., 2014). 5,6-dichlorobenzimidazole 1-beta-D-ribofuranoside (DRB) is added to cells before elongation to inhibit RNAPII transiently, allowing synchronized transcriptional initiation throughout the genome. Upon removal of DRB, Br-UTP is added instead of UTP, along with other nucleotides. After cell lysis, RNA is isolated and fragmented. Next, bromouridine-tagged RNA is immunoseparated from total RNA using magnetic beads coated with anti-BrdU antibodies. cDNA libraries are generated, using the TruSeq RNA library preparation protocol, and then sequenced.
Advantages:
- Quantifies RNA elongation rate throughout the whole genome
- Newly transcribed RNA molecules are tagged through their entire length
Disadvantages:
- Limited to cell cultures and other artificial systems, due to the requirement for incubation in the presence of labeled nucleotides
- Bru-Seq must be performed in conjunction with Bru-DRB-Seq for accurate data analysis
Reagents:
Illumina Library prep and Array Kit Selector
Reviews:
Jonkers I. and Lis J. T. Getting up to speed with transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015;16:167-177
References:
Veloso A., Kirkconnell K. S., Magnuson B., et al. Rate of elongation by RNA polymerase II is associated with specific gene features and epigenetic modifications. Genome Res. 2014;24:896-905
Related
History: BruDRB-Seq
Revision by sbrumpton on 2017-06-21 07:50:23 - Show/Hide
Bromouridine 5,6-dichlorobenzimidazole1-b-D-ribofuranoside Sequencing

BruDRB-Seq reports the elongation rate of RNAPII (Veloso et al., 2014). 5,6-dichlorobenzimidazole 1-beta-D-ribofuranoside (DRB) is added to cells before elongation to inhibit RNAPII transiently, allowing synchronized transcriptional initiation throughout the genome. Upon removal of DRB, Br-UTP is added instead of UTP, along with other nucleotides. After cell lysis, RNA is isolated and fragmented. Next, bromouridine-tagged RNA is immunoseparated from total RNA using magnetic beads coated with anti-BrdU antibodies. cDNA libraries are generated, using the TruSeq RNA library preparation protocol, and then sequenced.
Advantages:- Quantifies RNA elongation rate throughout the whole genome
- Newly transcribed RNA molecules are tagged through their entire length
Disadvantages:- Limited to cell cultures and other artificial systems, due to the requirement for incubation in the presence of labeled nucleotides
- Bru-Seq must be performed in conjunction with Bru-DRB-Seq for accurate data analysis
Reagents:Illumina Library prep and Array Kit SelectorReviews:Jonkers I. and Lis J. T. Getting up to speed with transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015;16:167-177References:Veloso A., Kirkconnell K. S., Magnuson B., et al. Rate of elongation by RNA polymerase II is associated with specific gene features and epigenetic modifications. Genome Res. 2014;24:896-905
