PAIR
Peptide Nucleic Acid (PNA)-Assisted Identification of RNA Binding Proteins
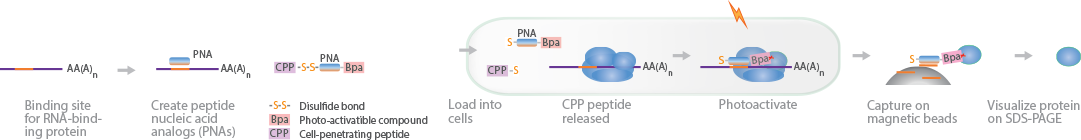
PAIR uses PNAs to capture RBPs in vivo (Zielinski et al., 2006) (Zeng et al., 2006). The PNAs are coupled to a cell membrane-penetrating peptide (CPP) to deliver PNAs efficiently into living cells, as well as a photoactivatable compound, p-benzoylphenylalanine (Bpa). The cells are illuminated with UV light, activating the Bpa on the PNA to form covalent bonds with the RBP. Next, the cells are lysed, and the RNA complexes are captured on magnetic beads. The proteins can be reverse-crosslinked and visualized by denaturing gel electrophoresis, while the RNA strands are sequenced.
Advantages:
- Identifies RNA-protein interactions in vivo
- Commercial PNAs can be purchased, eliminating the need for PNA design
Disadvantages:
- Custom PNA design can cause problems with low protein yield
- Not yet adopted widely by the scientific community
Reagents:
Illumina Library prep and Array Kit Selector
Reviews:
Jazurek M., Ciesiolka A., Starega-Roslan J., Bilinska K. and Krzyzosiak W. J. Identifying proteins that bind to specific RNAs – focus on simple repeat expansion diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:9050-9070
McHugh C. A., Russell P. and Guttman M. Methods for comprehensive experimental identification of RNA-protein interactions. Genome Biol. 2014;15:203
References:
Zielinski J., Kilk K., Peritz T., et al. In vivo identification of ribonucleoprotein-RNA interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:1557-1562
Related
History: PAIR
Revision by sbrumpton on 2017-06-21 07:50:22 - Show/Hide
Peptide Nucleic Acid (PNA)-Assisted Identification of RNA Binding Proteins

PAIR uses PNAs to capture RBPs in vivo (Zielinski et al., 2006) (Zeng et al., 2006). The PNAs are coupled to a cell membrane-penetrating peptide (CPP) to deliver PNAs efficiently into living cells, as well as a photoactivatable compound, p-benzoylphenylalanine (Bpa). The cells are illuminated with UV light, activating the Bpa on the PNA to form covalent bonds with the RBP. Next, the cells are lysed, and the RNA complexes are captured on magnetic beads. The proteins can be reverse-crosslinked and visualized by denaturing gel electrophoresis, while the RNA strands are sequenced.
Advantages:- Identifies RNA-protein interactions in vivo
- Commercial PNAs can be purchased, eliminating the need for PNA design
Disadvantages:- Custom PNA design can cause problems with low protein yield
- Not yet adopted widely by the scientific community
Reagents:Illumina Library prep and Array Kit SelectorReviews:Jazurek M., Ciesiolka A., Starega-Roslan J., Bilinska K. and Krzyzosiak W. J. Identifying proteins that bind to specific RNAs - focus on simple repeat expansion diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:9050-9070McHugh C. A., Russell P. and Guttman M. Methods for comprehensive experimental identification of RNA-protein interactions. Genome Biol. 2014;15:203References:Zielinski J., Kilk K., Peritz T., et al. In vivo identification of ribonucleoprotein-RNA interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:1557-1562
